Trace Elements Market Analysis
I,Analysis of non-ferrous metals
Week-on-week: Month-on-month:
| Units | Week 1 of December | Week 2 of December | Week-on-week changes | November average price | The average price up to December 12 | Month-on-month changes | Current price as of December 16 | |
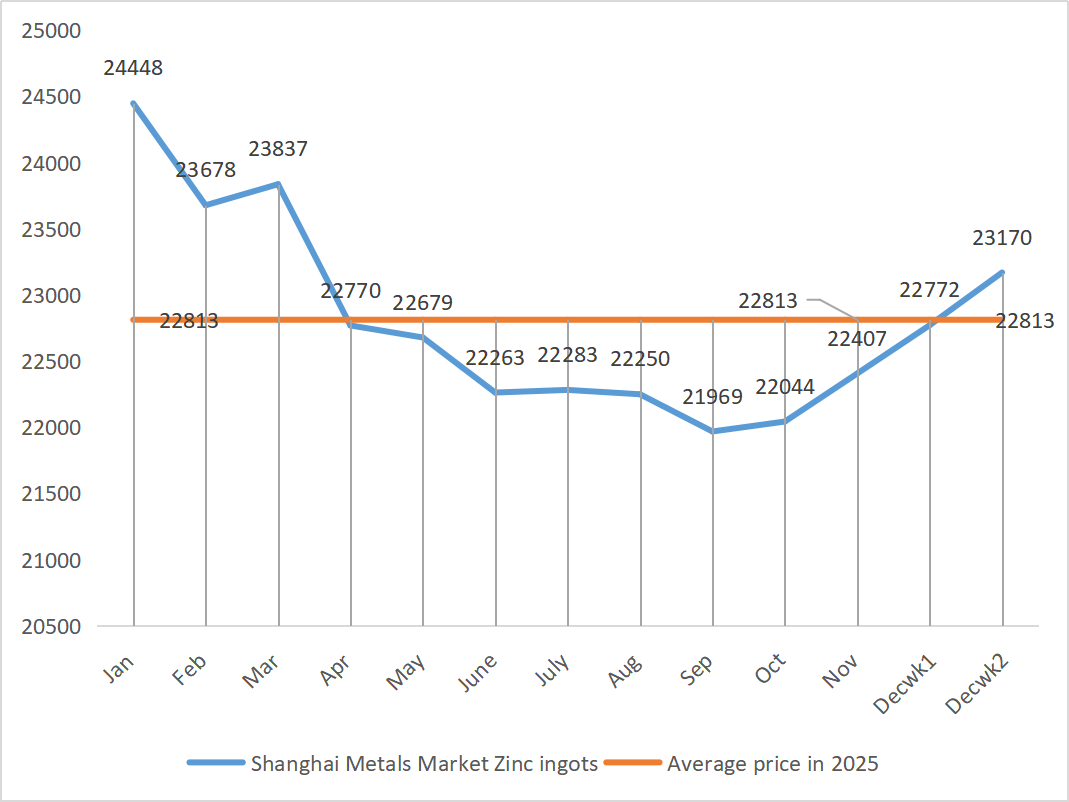
| Shanghai Metals Market # Zinc ingots | Yuan/ton |
22772 |
23170 |
↑398 |
22407 |
22971 |
↑564 |
23180 |
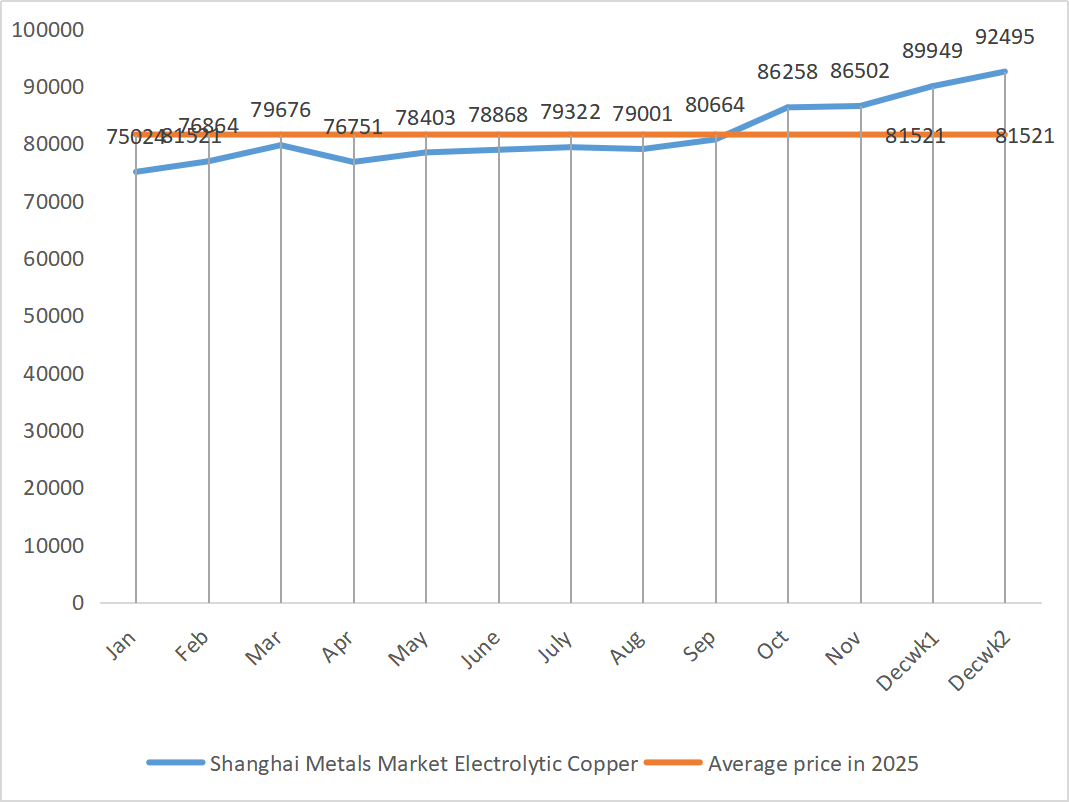
| Shanghai Metals Network # Electrolytic copper | Yuan/ton |
89949 |
90495 |
↑2546 |
86502 |
91222 |
↑4720 |
91700 |
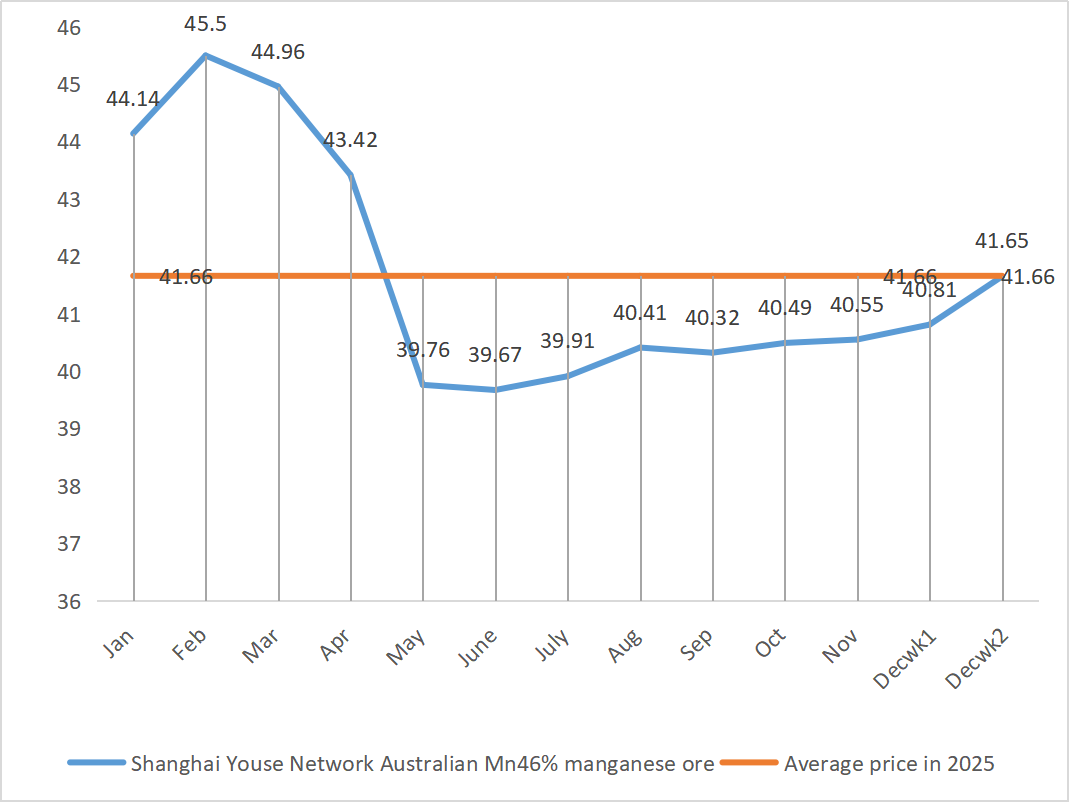
| Shanghai Metals Network Australia
Mn46% manganese ore |
Yuan/ton |
40.81 |
41.65 |
↑0.84 |
40.55 |
41.23 |
↑0.68 |
41.85 |
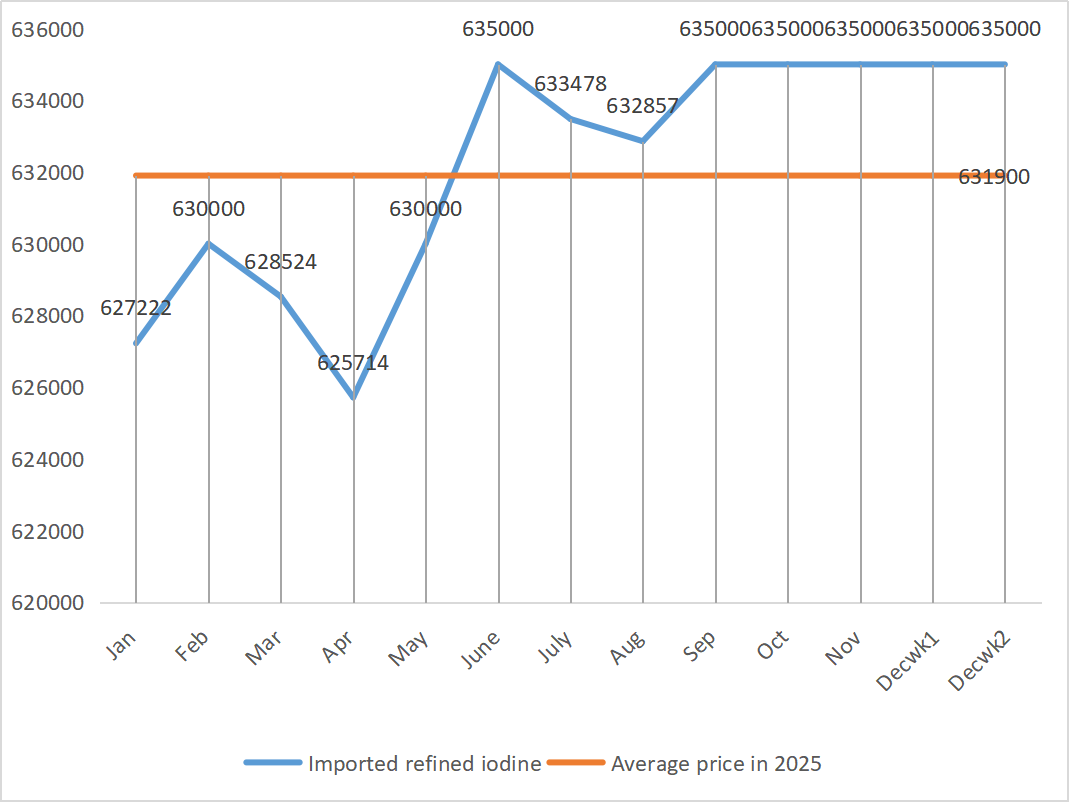
| The price of imported refined iodine by Business Society | Yuan/ton |
635000 |
635000 |
- |
635000 |
635000 |
|
635000 |
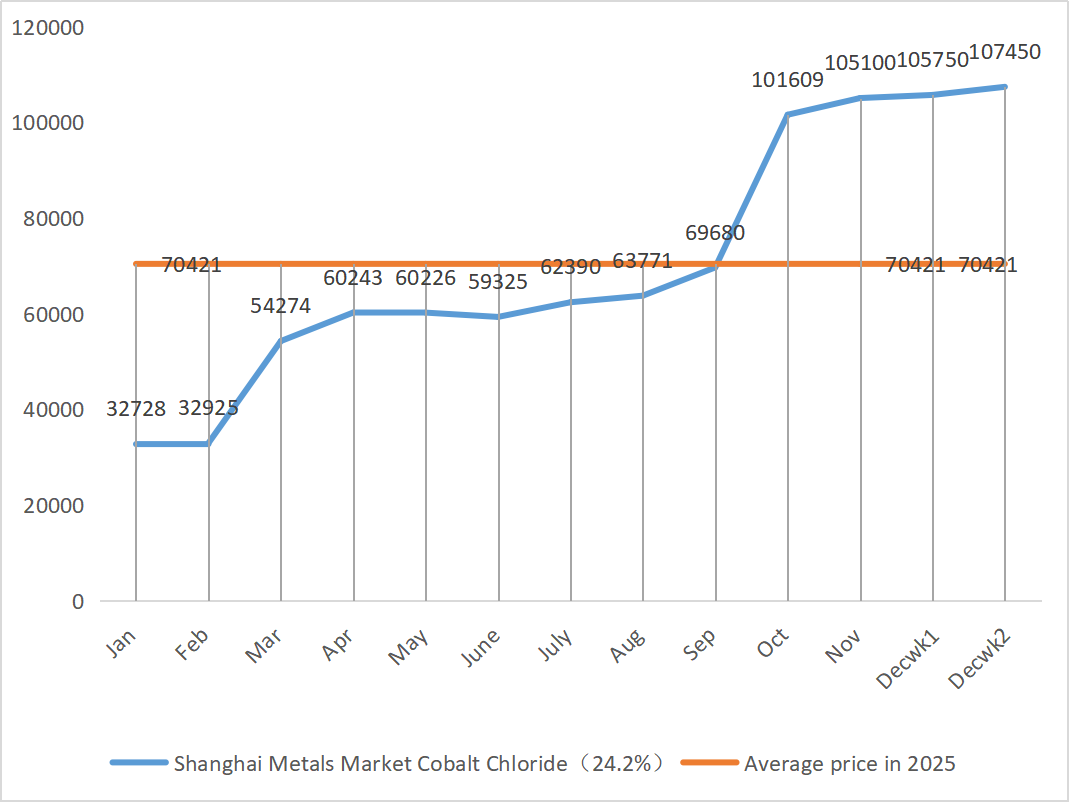
| Shanghai Metals Market Cobalt Chloride
(co≥24.2%) |
Yuan/ton |
105750 |
107450 |
↑1700 |
105100 |
106600 |
↑1500 |
110750 |
| Shanghai Metals Market Selenium Dioxide | Yuan per kilogram |
114 |
108 |
↓6 |
113.5 |
111 |
↓2.5 |
107.5 |
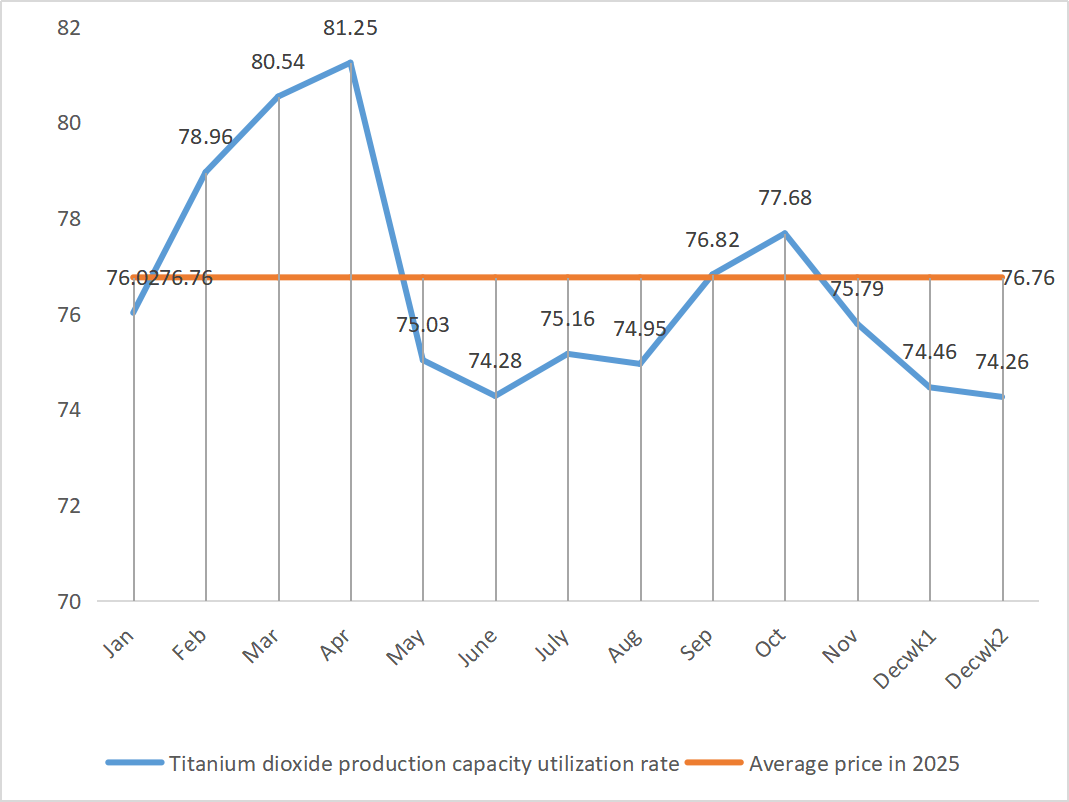
| Capacity utilization rate of titanium dioxide manufacturers | % |
74.46 |
74.26 |
↓0.2 |
75.97 |
74.36 |
↓1.61 |
1)Zinc sulfate
① Raw materials: Zinc hypooxide: The transaction coefficient and zinc price have both climbed, and the cost pressure of core raw materials remains significant.
The foreign Federal Reserve cut interest rates by 25 basis points, largely in line with market expectations. Coupled with the release of long-term positive signals domestically, both domestic and foreign positive information have boosted non-ferrous metal prices. There are no obvious highlights in domestic consumption at present, and the supply side is gradually tightening. Under the combined influence of macroeconomics and fundamentals, Shanghai zinc is expected to remain strongly volatile next week at around 23,800 yuan per ton.
② Sulfuric acid: The domestic sulfur spot market continued the upward trend seen in November in December, pushing up at high levels. Looking back over the past two months, the soaring sulfur prices have been the core driver, and the cost inversion has forced price hikes. Sulfur is the core raw material for sulfuric acid production (about 0.33 tons of sulfur are consumed to produce one ton of sulfuric acid), and domestic sulfur prices have risen sharply in two months, with an increase of up to 130% compared to the beginning of the year. The global sulfur supply pattern has changed dramatically. The Russia-Ukraine conflict has imposed export bans and Kazakhstan’s export volume has declined, widening the international supply gap. Domestic port inventories have dropped to 2.2 million tons (below reasonable level), coupled with strengthened pricing power in the Middle East and panic buying in countries such as Indonesia/India. The cost transmission directly forced the price of sulfuric acid to rise passively; At the same time, the price of pyrite was also at a high level, further reinforcing the cost support of the ore acid. Overall, it is expected that sulfuric acid will continue to rise in the short term, and prices may continue to increase in some areas.
On Monday, the operating rate of water zinc sulfate producers was 83%, up 9% from the previous week; Capacity utilization was 63%, up 2% from the previous week. Prices are expected to rise again, driven by both high production costs and improved terminal demand. Customers are advised to lock in orders in advance based on their inventory and delivery cycle to control supply chain and cost risks.
2)Manganese sulfate
In terms of raw materials: ① The manganese ore market continues to show a strong upward trend
② Sulfuric acid prices remain stable at a high level and are expected to strengthen.
This week, the operating rate of manganese sulfate producers was 90%, up 20% from the previous week; Capacity utilization was 62%, up 15% from the previous week. Driven by costs, manganese sulfate prices are expected to follow suit if sulfuric acid prices continue to rise. Quotations from major manufacturers are generally raised accordingly. Customers are advised to buy on demand.
3)Ferrous sulfate
In terms of raw materials: As a by-product of titanium dioxide, its supply is restricted by the main industry. The current high inventory and sluggish sales in the titanium dioxide industry, along with the shutdown of some manufacturers, have directly led to a reduction in the output of ferrous sulfate. Meanwhile, the demand for lithium iron phosphate is stable and continues to divert some raw materials, exacerbating the tight supply of feed-grade products.
Ferrous sulfate prices are more likely to rise than fall. Against the backdrop of strong support from raw material costs and the suspension of quotations in some regions, it is expected that ferrous sulfate prices will show an upward trend in the medium and short term.
It is suggested that the demand side purchase according to its own production situation.
4)Copper sulfate/basic copper chloride
In terms of fundamentals, growing concerns over the AI bubble triggered a full-blown sell-off of risky assets. There is a divergence within the Fed over the policy path, with some officials believing that further rate cuts need more confirmation; Other officials stressed that rates should be kept tight enough to sustain inflationary pressures. This has cooled expectations of a “fast easing cycle.” If policy signals are hawkish, the dollar could rebound in phases, thereby suppressing copper prices. Global stock markets fell on a large scale today, with high risk aversion in the market and funds accelerating their withdrawal from the copper market, with some funds flowing to safe-haven assets such as gold. Fundamentals: Disruptions from overseas mines have not ceased, and large amounts of copper are being shipped to the United States, leading to tight supply in other parts of the world. The tight supply situation still provides bottom support for copper prices. But domestic physical consumption is sluggish, and the accumulation of inventories is putting further pressure, suggesting that demand may face temporary pressure. The spot market is active in buying at low prices, the spot premium continues to be under pressure to be lowered, holders have a strong willingness to sell, and there is an increase in low-priced supplies. Copper prices are expected to remain at a high level amid sharp fluctuations.
On the macro level, the liquidity easing dividend from the Fed’s rate cuts remains, but market concerns over the pace of the global economic recovery have cooled risk appetite, which has passed on to copper prices.
Overall, copper prices are likely to remain in a range of 91,000-94,000 yuan per ton in the short term (within the year), with demand for buying at low prices after a pullback at high levels expected to support prices. Attention should be paid to the progress of inventory reduction and the policy direction of the Federal Reserve.
Customers are advised to take advantage of their own inventories to stock up when copper prices fall back to a relatively low level, so as to ensure supply while controlling costs.
5)Magnesium sulfate/magnesium oxide
In terms of raw materials: Currently, sulfuric acid in the north is stable at a high level.
Magnesium oxide and magnesium sulfate prices have risen. The impact of magnesite resource control, quota restrictions and environmental rectification has led to many enterprises producing based on sales. Light-burned magnesium oxide enterprises shut down on Friday due to capacity replacement policies and the increase in sulfuric acid prices, and the prices of magnesium sulfate and magnesium oxide rose in the short term. It is recommended to stock up appropriately.
6)Calcium iodate
Raw materials: The price of refined iodine rose slightly in the fourth quarter. The supply of calcium iodate is tight. Some iodide manufacturers have suspended production or limited production. The supply of iodide is expected to remain stable and slightly upward in the long term. It is recommended to stock up appropriately.
7)Sodium selenite
In terms of raw materials: The selenium market was weak at the end of the year, with light transactions. The price center of crude selenium and disselenium shifted downward, while the prices of selenium powder and selenium tablets remained unchanged. Terminal restocking is coming to an end, speculative funds are on the sidelines, and prices are under short-term pressure. Buy on demand
8)Cobalt chloride
The shortage of raw materials has shifted from expectation to reality, and producers are maintaining strong quotations supported by high costs. The cobalt chloride market has picked up. The tight supply of raw materials combined with the release of downstream stockpiling demand has increased market activity and prices have shown a slight upward trend, with short-term positive support continuing. Stock up appropriately based on demand. Stock appropriately according to demand.
9)Cobalt salt/potassium chloride/potassium carbonate/calcium formate/iodide
1. Cobalt salts: Raw material costs: The Democratic Republic of the Congo, as the world’s largest producer of cobalt, accounts for 75%-76% of global cobalt production. The country officially implemented an export quota system starting October 16, 2025, with an export cap of only 18,125 tons for the remainder of 2025 and a quota of 96,600 tons per year for 2026-2027, a 56% reduction from actual exports in 2024. The policy has led to a reduction of about 200,000 tons in global cobalt supply, or 40% of annual demand. More seriously, as of early December, the export approval process remains unfinished and actual shipments are at a standstill, with the earliest expected resumption in the first quarter of 2026. Domestic electrolytic cobalt social inventories have dropped to a record low of 2,500-2,800 tons, only enough to meet downstream demand for 8-10 days, the lowest for the same period in nearly five years, and low inventories amplify price fluctuations. Attention should be paid to the implementation of the quota policy in the Democratic Republic of the Congo, the progress of the release of new capacity in Indonesia, and the pace of increasing demand in emerging fields such as humanoid robots.
2. Potassium chloride: Overall stability, local fluctuations: Recently, the potassium chloride market has been mainly stabilizing and consolidating. There are signs of a rebound in the prices of some products that have fallen significantly earlier, but there are still certain difficulties in implementing high prices. In the long term, the possibility of a significant price increase is low
3. Calcium formate prices were stable this week. Calcium formate prices are expected to rise in the short term as raw formic acid plants are shut down for maintenance in December until the end of the month due to raw material shortages.
4 Iodide prices were stable this week compared with last week.
Post time: Dec-17-2025