Glycinate Chelated Magnesium Feed Grade Amino Acid Glycine Chelate
Magnesium is an essential component of animal bone and dental structures, primarily functioning in concert with potassium and sodium to regulate neuromuscular excitability. Magnesium glycinate exhibits excellent bioavailability and serves as a premium magnesium source in animal nutrition. It partakes in energy metabolism, neuromuscular regulation, and enzymatic activity modulation, thereby aiding stress mitigation, mood stabilization, growth promotion, reproductive performance enhancement, and skeletal health improvement. Moreover, magnesium glycinate is recognized as GRAS (Generally Recognized As Safe) by the U.S. FDA and is listed in the EU EINECS inventory (No. 238‑852‑2). It complies with the EU Feed Additives Regulation (EC 1831/2003) regarding the use of chelated trace elements, ensuring robust international regulatory conformity.

Product Information
Product Name: Feed‑Grade Glycinate‑Chelated Magnesium
Molecular Formula: Mg(C2H5NO2)SO4·5H2O
Molecular Weight: 285
CAS No.: 14783‑68‑7
Appearance: White crystalline powder; free‑flowing, non‑caking
Physicochemical Specifications
|
Item |
Indicator |
|
Total glycine content, % |
≥21.0 |
|
Free glycine content, % |
≤1.5 |
|
Mg2+, (%) |
≥10.0 |
|
Total arsenic(subject to As), mg/kg |
≤5.0 |
|
Pb (subject to Pb), mg/kg |
≤5.0 |
|
Water content, % |
≤5.0 |
|
Fineness (Passing rate W=840μm test sieve), % |
≥95.0 |
Product Benefits
1) Stable Chelation, Preserves Nutrient Integrity
Glycine, a small‑molecule amino acid, forms a stable chelate with magnesium, effectively preventing deleterious interactions between magnesium and fats, vitamins, or other nutrients.
2) High Bioavailability
The magnesium‑glycinate chelate utilizes amino acid transport pathways, enhancing intestinal uptake efficiency compared to inorganic magnesium sources such as magnesium oxide or magnesium sulfate.
3) Safe and Environmentally Friendly
High bioavailability reduces excretion of trace elements, mitigating environmental impact.
Product efficacy
1) Stabilizes the central nervous system and alleviates stress responses.
2) Acts synergistically with calcium and phosphorus to support robust skeletal development.
3) Prevents magnesium‑deficiency disorders in animals, such as muscle spasms and postpartum paresis.
Product applications
1.Pigs
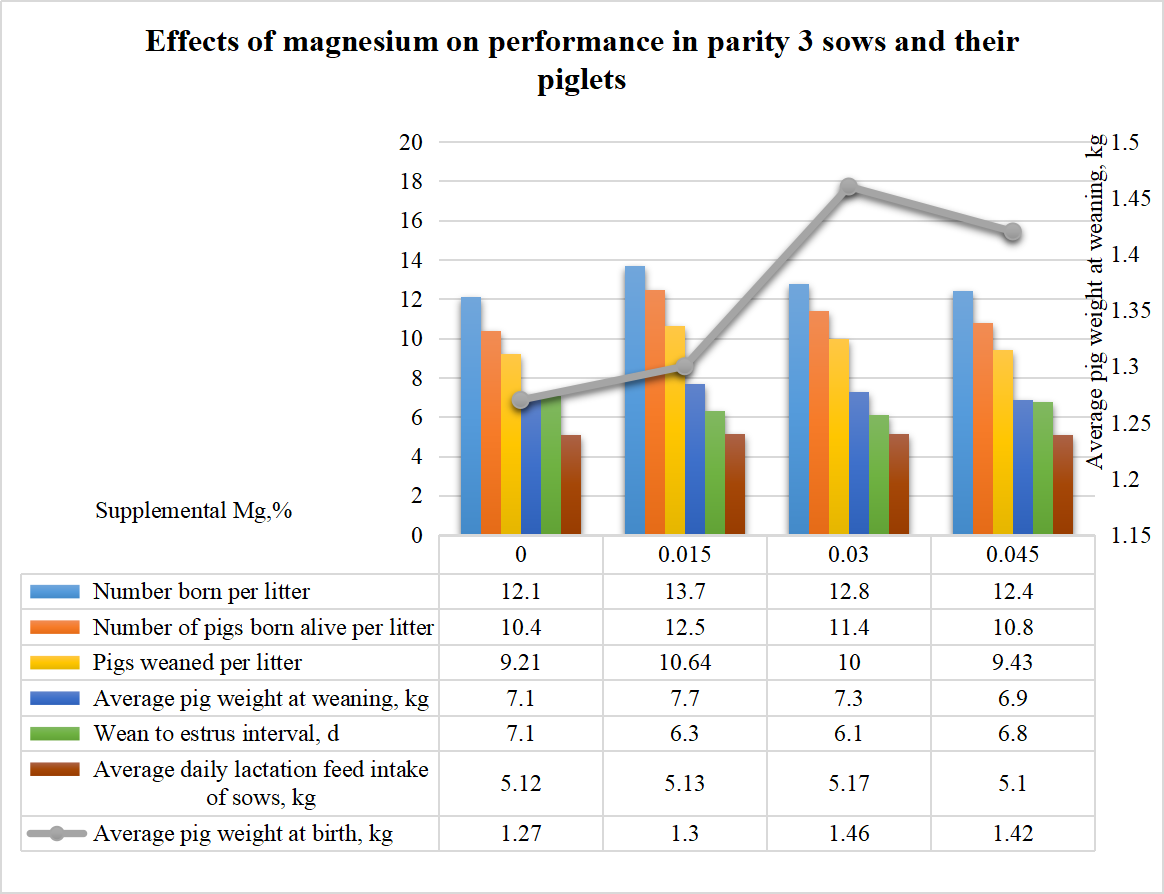
Dietary supplementation of 0.015 % to 0.03 % magnesium has been shown to significantly improve sow reproductive performance, shorten the weaning‑to‑estrus interval, and enhance piglet growth and health. Studies indicate that magnesium supplementation is particularly beneficial for high‑producing sows, especially as their body magnesium reserves decline with age, making dietary magnesium inclusion increasingly important.
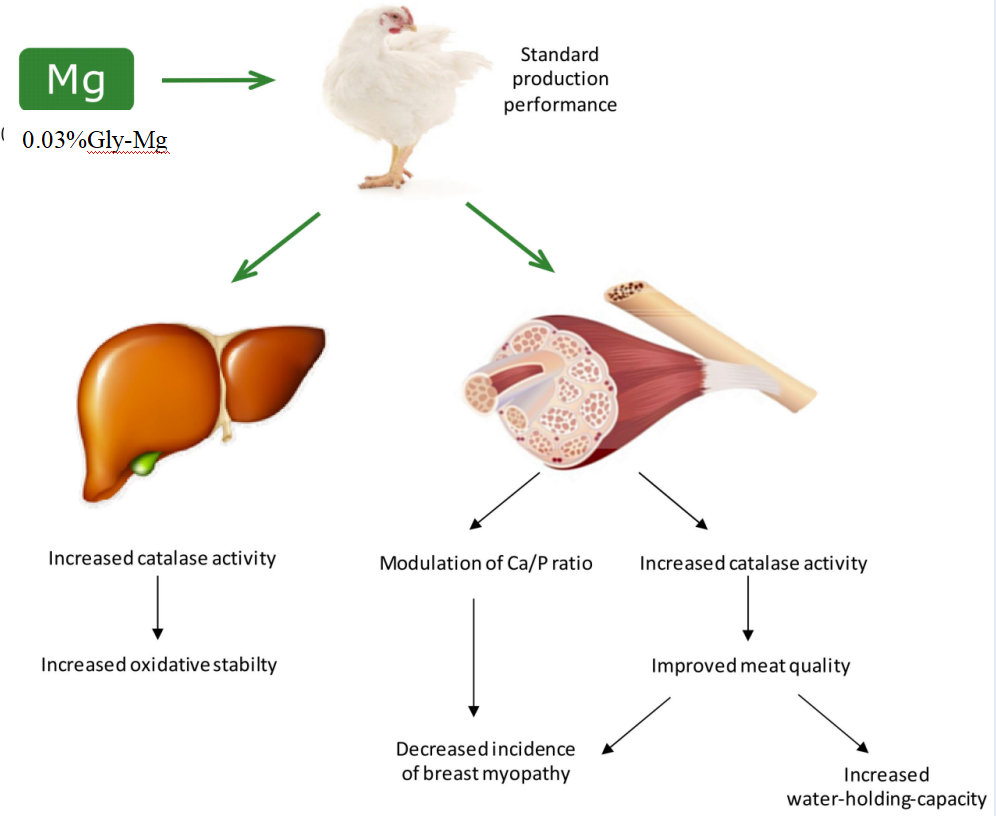
Inclusion of 3,000 ppm organic magnesium in broiler diets under heat‑stress and oxidized‑oil challenge conditions did not adversely affect growth performance, but it did markedly reduce the incidence of woody breast and white striping myopathies. Concurrently, meat water‑holding capacity was improved and muscle color quality enhanced. Additionally, antioxidant enzyme activities in both liver and plasma were significantly elevated, indicating strengthened antioxidative capacity.
3.Laying Hens
Research demonstrates that magnesium deficiency in laying hens leads to reduced feed intake, egg production, and hatchability, with the drop in hatchability closely linked to hypomagnesemia in the hen and decreased magnesium content within the egg. Supplementation to reach a dietary level of 355 ppm total magnesium (approximately 36 mg Mg per bird per day) effectively maintains high egg‑laying performance and hatchability, thereby boosting production efficiency.
4.Ruminants
Magnesium inclusion in ruminant rations substantially enhances ruminal cellulose digestion. Magnesium deficiency reduces both fiber digestibility and voluntary feed intake; restoration of adequate magnesium reverses these effects, improving digestive efficiency and feed consumption. Magnesium plays a critical role in supporting rumen microbial activity and fiber utilization.
Table 1 Effect of magnesium and sulfur upon in vivo cellulose digestion by steers and in vitro digestion using rumen inoculum from steers
|
Period |
Ration treatment |
|||
|
Complete |
Without Mg |
Without S |
Without Mg and S |
|
|
Cellulose digested in vivo(%) |
||||
|
1 |
71.4 |
53.0 |
40.4 |
39.7 |
|
2 |
72.8 |
50.8 |
12.2 |
0.0 |
|
3 |
74.9 |
49.0 |
22.8 |
37.6 |
|
4 |
55.0 |
25.4 |
7.6 |
0.0 |
|
Mean |
68.5a |
44.5b |
20.8bc |
19.4bc |
|
Cellulose digested in vitro (%) |
||||
|
1 |
30.1 |
5.9 |
5.2 |
8.0 |
|
2 |
52.6 |
8.7 |
0.6 |
3.1 |
|
3 |
25.3 |
0.7 |
0.0 |
0.2 |
|
4 |
25.9 |
0.4 |
0.3 |
11.6 |
|
Mean |
33.5a |
3.9b |
1.6b |
5.7b |
Note: Different superscript letters significantly different (P < 0.01).
5.Aqua Animals
Studies in Japanese seabass have shown that dietary supplementation with magnesium glycinate significantly enhances growth performance and feed conversion efficiency. It also promotes lipid deposition, modulates expression of fatty‑acid–metabolizing enzymes, and influences overall lipid metabolism, thereby improving both fish growth and fillet quality. (IM:MgSO4;OM:Gly-Mg)
Table 2 Effects of diets containing different magnesium levels on the enzyme activity of liver of Japanese seabass in freshwater
|
Dietary Mg Level (mg Mg/kg) |
SOD (U/mg protein) |
MDA (nmol/mg protein) |
GSH‑PX (g/L) | T‑AOC (mg protein) | CAT (U/g protein) |
|
412 (Basic) |
84.33±8.62 a |
1.28±0.06 b |
38.64±6.00 a |
1.30±0.06 a |
329.67±19.50 a |
|
683 (IM) |
90.33±19.86 abc |
1.12±0.19 b |
42.41±2.50 a |
1.35±0.19 ab |
340.00±61.92 ab |
|
972 (IM) |
111.00±17.06 bc |
0.84±0.09 a |
49.90±2.19 bc |
1.45±0.07 bc |
348.67±62.50 ab |
|
972 (IM) |
111.00±17.06 bc |
0.84±0.09 a |
49.90±2.19 bc |
1.45±0.07 bc |
348.67±62.50 ab |
|
702 (OM) |
102.67±3.51 abc |
1.17±0.09 b |
50.47±2.09 bc |
1.55±0.12 cd |
406.67±47.72 b |
|
1028 (OM) |
112.67±8.02 c |
0.79±0.16 a |
54.32±4.26 c |
1.67±0.07 d |
494.33±23.07 c |
|
1935 (OM) |
88.67±9.50 ab |
1.09±0.09 b |
52.83±0.35 c |
1.53±0.16 c |
535.00±46.13 c |
l Usage & Dosage
Applicable Species: Farm animals
1) Dosage Guidelines: Recommended inclusion rates per tonne of complete feed (g/t, expressed as Mg2+):
|
Pigs |
Poultry |
Cattle |
Sheep |
Aquatic animal |
|
100-400 |
200-500 |
2000-3500 |
500-1500 |
300-600 |
2) Synergistic Trace‑Mineral Combinations
In practice, magnesium glycinate is often formulated alongside other amino‑acid–chelated minerals to create a “functional micro‑mineral system,” targeting stress modulation, growth promotion, immune regulation, and reproductive enhancement.
|
Mineral Type |
Typical Chelate |
Synergistic Benefit |
|
Copper |
Copper glycinate, copper peptides |
Anti‑anemic support; enhanced antioxidant capacity |
|
Iron |
Iron glycinate |
Hematinic effect; growth promotion |
|
Manganese |
Manganese glycinate |
Skeletal strengthening; reproductive support |
|
Zinc |
Zinc glycinate |
Immune enhancement; growth stimulation |
|
Cobalt |
Cobalt peptides |
Rumen microflora modulation (ruminants) |
|
Selenium |
L-Selenomethionine |
Stress resilience; meat quality preservation |
3) Recommended Export‑Grade Product Blends
l Pigs
Co‑administration of magnesium glycinate with an organic iron peptide (“Peptide‑Hematine”) employs dual pathways (“organic iron + organic magnesium”) to synergistically support hematopoiesis, neuromuscular development, and immune function in early‑weaned piglets, mitigating weaning stress.
Recommended Inclusion: 500 mg/kg Peptide‑Hematine + 300 mg/kg Magnesium Glycinate
l Layers
“YouDanJia” is an organic trace‑mineral premix for laying hens—typically containing chelated zinc, manganese, and iron—to improve eggshell quality, laying rate, and immunity. When used in combination with magnesium glycinate, it provides complementary trace‑mineral nutrition, stress management, and laying‑performance optimization.
Recommended Inclusion: 500 mg/kg YouDanJia + 400 mg/kg Magnesium Glycinate
l Packaging: 25 kg per bag, inner and outer multilayer polyethylene liners.
l Storage: Store in a cool, dry, and well‑ventilated area. Keep sealed and protected from moisture.
l Shelf Life: 24 months.
Top Choice of International Grop
Sustar group has decades-long partnership with CP Group, Cargill, DSM, ADM,Deheus ,Nutreco,New Hope ,Haid,Tongwei and some other TOP 100 big feed company.

Our Superiority


A Reliable Partner
Research and development capabilities
Integrating the talents of the team to build Lanzhi Institute of Biology
In order to promote and influence the development of livestock industry at home and abroad, Xuzhou Animal Nutrition Institute , Tongshan District Government, Sichuan Agricultural University and Jiangsu Sustar, the four sides established Xuzhou Lianzhi Biotechnology Research Institute in December 2019.
Professor Yu Bing of Animal Nutrition Research Institute of Sichuan Agricultural University served as the dean, Professor Zheng Ping and Professor Tong Gaogao served as the deputy dean. Many professors of Animal Nutrition Research Institute of Sichuan Agricultural University helped the expert team to accelerate the transformation of scientific and technological achievements in the animal husbandry industry and promote the development of the industry.


As a member of the National Technical Committee for Standardization of Feed Industry and the winner of China Standard Innovation Contribution Award, Sustar has participated in drafting or revising 13 national or industrial product standards and 1 method standard since 1997.
Sustar has passed the ISO9001 and ISO22000 system certification FAMI-QS product certification, obtained 2 invention patents, 13 utility model patents, accepted 60 patents, and passed the "Standardization of intellectual property management system", and was recognized as a national-level new high-tech enterprise.

Our premixed feed production line and drying equipment are in the leading position in the industry. Sustar has high performance liquid chromatograph, atomic absorption spectrophotometer, ultraviolet and visible spectrophotometer, atomic fluorescence spectrophotometer and other major testing instruments, complete and advanced configuration.
We has more than 30 animal nutritionists, animal veterinarians, chemical analysts, equipment engineers and senior professionals in feed processing, research and development, laboratory testing, to provide customers with a full range of services from formula development, product production, inspection, testing, product program integration and application and so on.
Quality inspection
We provide test reports for each batch of our products, such as heavy metals and microbial residues. Each batch of dioxins and PCBS complies with EU standards. To ensure safety and compliance.
Assist customers to complete the regulatory compliance of feed additives in different countries, such as the registration and filing in the EU, USA, South America, Middle East and other markets.

Production Capacity

Main product production capacity
Copper sulfate-15,000 tons/year
TBCC -6,000 tons/year
TBZC -6,000 tons/year
Potassium chloride -7,000 tons/year
Glycine chelate series -7,000 tons/year
Small peptide chelate series-3,000 tons/year
Manganese sulfate -20,000 tons /year
Ferrous sulfate-20,000 tons/year
Zinc sulfate -20,000 tons/year
Premix (Vitamin/Minerals)-60,000 tons/year
More than 35 years history with five factory
Sustar group has five factories in China ,with annual capacity up to 200,000 tonns, covering totally 34,473 square meters,220 employees.And we’re an FAMI-QS/ISO/GMP certified company .
Customized Services

Customize Purity Level
Our company has a number of products have a wide variety of purity levels, especially to support our customers to do customized services, according to your needs. For example, our product DMPT is available in 98%, 80%, and 40% purity options; Chromium picolinate can be provided with Cr 2%-12%; and L-selenomethionine can be provided with Se 0.4%-5%.

Custom Packaging
According to your design requirements, you can customize the logo, size, shape, and pattern of the outer packaging
No one-size-fits-all formula? We tailor it for you!
We are well aware that there are differences in raw materials, farming patterns and management levels in different regions. Our technical service team can provide you with one to one formula customization service.


Success Case

Positive Review

Various Exhibitions we Attend